What constitutes a ‘document’ and how does it function?
According to the Oxford English Dictionary, the etymological origin is the Latin ‘documentum’, meaning ‘lesson, proof, instance, specimen’. As a verb, it is ‘to prove or support (something) by documentary evidence’, and ‘to provide with documents’. The online version of the OED includes a draft addition, whereby a document (as a noun) is ‘a collection of data in digital form that is considered a single item and typically has a unique filename by which it can be stored, retrieved, or transmitted (as a file, a spreadsheet, or a graphic)’. The current use of the noun ‘document’ is defined as ‘something written, inscribed, etc., which furnishes evidence or information upon any subject, as a manuscript, title-deed, tomb-stone, coin, picture, etc.’ (emphasis added).
Both ‘something’ and that first ‘etc.’ leave ample room for discussion. A document doubts whether it functions as something unique, or as something reproducible. A passport is a document, but a flyer equally so. Moreover, there is a circular reasoning: to document is ‘to provide with documents’. Defining (the functioning of) a document most likely involves ideas of communication, information, evidence, inscriptions, and implies notions of objectivity and neutrality – but the document is neither reducible to one of them, nor is it equal to their sum. It is hard to pinpoint it, as it disperses into and is affected by other fields: it is intrinsically tied to the history of media and to important currents in literature, photography and art; it is linked to epistemic and power structures. However ubiquitous it is, as an often tangible thing in our environment, and as a concept, a document deranges.
the-documents.org continuously gathers documents and provides them with a short textual description, explanation,
or digression, written by multiple authors. In Paper Knowledge, Lisa Gitelman paraphrases ‘documentalist’ Suzanne Briet, stating that ‘an antelope running wild would not be a document, but an antelope taken into a zoo would be one, presumably because it would then be framed – or reframed – as an example, specimen, or instance’. The gathered files are all documents – if they weren’t before publication, they now are. That is what the-documents.org, irreversibly, does. It is a zoo turning an antelope into an ‘antelope’.
As you made your way through the collection,
the-documents.org tracked the entries you viewed.
It documented your path through the website.
As such, the time spent on the-documents.org turned
into this – a new document.
This document was compiled by ____ on 11.09.2023 17:27, printed on ____ and contains 15 documents on _ pages.
(https://the-documents.org/log/11-09-2023-5436/)
the-documents.org is a project created and edited by De Cleene De Cleene; design & development by atelier Haegeman Temmerman.
the-documents.org has been online since 23.05.2021.
- De Cleene De Cleene is Michiel De Cleene and Arnout De Cleene. Together they form a research group that focusses on novel ways of approaching the everyday, by artistic means and from a cultural and critical perspective.
www.decleenedecleene.be / info@decleenedecleene.be - This project was made possible with the support of the Flemish Government and KASK & Conservatorium, the school of arts of HOGENT and Howest. It is part of the research project Documenting Objects, financed by the HOGENT Arts Research Fund.
- Briet, S. Qu’est-ce que la documentation? Paris: Edit, 1951.
- Gitelman, L. Paper Knowledge. Toward a Media History of Documents.
Durham/ London: Duke University Press, 2014. - Oxford English Dictionary Online. Accessed on 13.05.2021.
‘Meunerie Duyckers & Conors, les nouveaux moulins’, better known as ‘De Nieuwe Molens’, is a flour mill established in 1897 in the north of Gent along the Verbindingskanaal. Due to increased production, the original 1897 building doubled in 1904.
Only the facade of the iconic warehouse has been preserved along with the recently renovated gasometers. The building is now part of the Tondeliersite. It has been converted into lofts and flats, and was extended with a new construction.
https://inventaris.onroerenderfgoed.be/erfgoedobjecten/18269

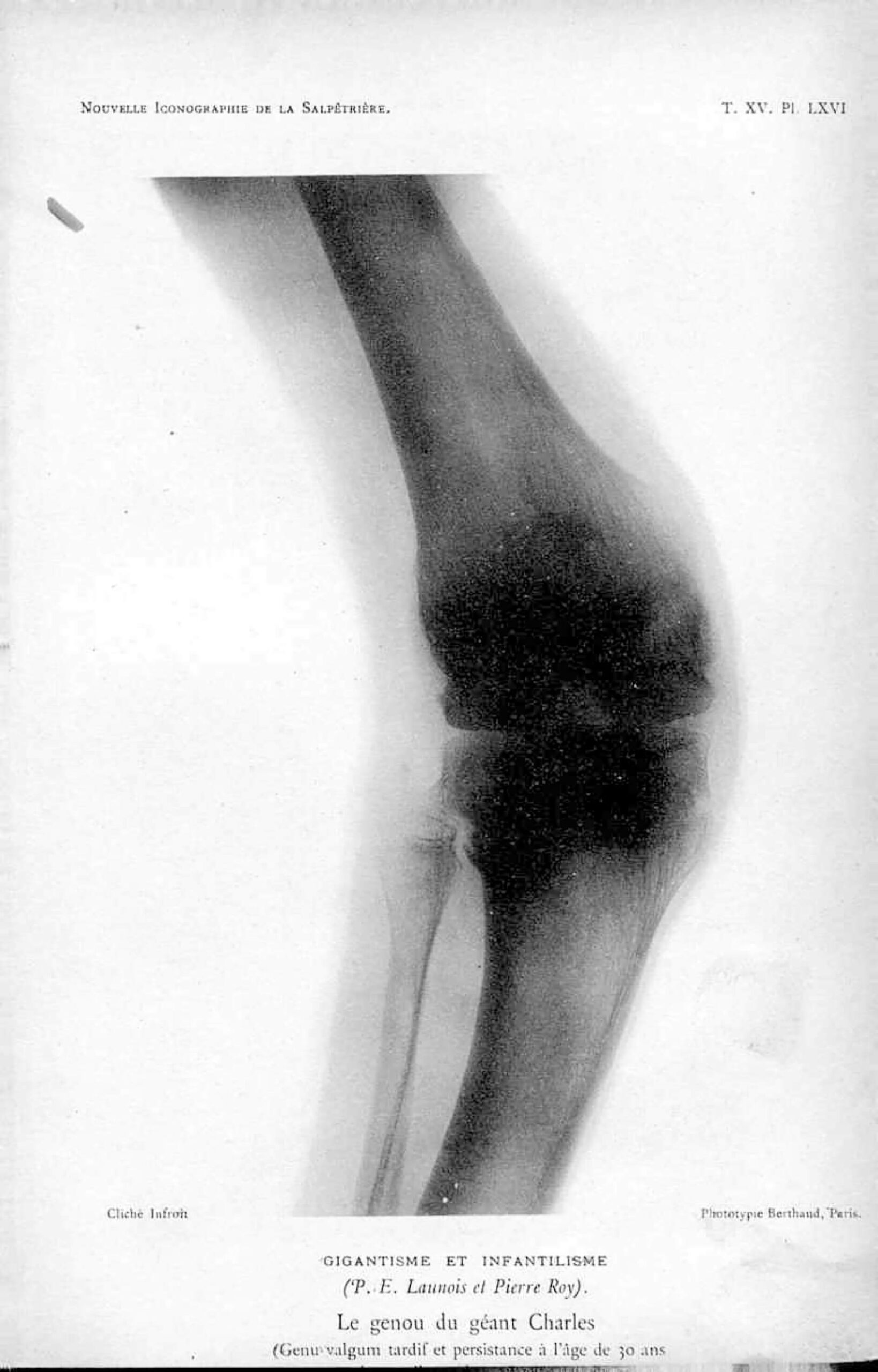
The scientific exactitude sought for in the Iconographie de la Salpêtrière and the Nouvelle Iconographie de la Salpêtrière, the (in)famous scientific publications stemming from Paris’ psychiatric hospital La Salpêtrière (1876-1918), lead to an abundance of photographic images in their pages. The photographs’ ideal: ‘Trace incontestable, incontestablement fidèle, durable, transmissible’.1 The ambition of exactitude results in cold, and often cruel depictions of patients. In the digitized version of the Sorbonne library’s copies, some photographs have left an imprint on the opposite page. The knee of Charles, ‘le géant’, adds an unwanted layer upon its measures on the opposite page, while the photograph of the knee itself loses ink.2
Didi-Huberman, G. Invention de l’hystérie. Paris: Macula, 2014, 72.
Launois, P.-E., Roy, P., ‘Gigantisme et infantilisme’, Nouvelle Iconographie de la Salpêtrière, Tome XV, 1902, 548, pl. LXVI, online: https://patrimoine.sorbonne-universite.fr/fonds/item/2613-nouvelle-iconographie-de-la-salpetriere-tome-15?offset=6

During the preparation of a seminar, I reread Pierre Bayard’s Qui a tué Roger Ackroyd? (2008). On the inside of the back cover, there’s an inscription: it appears I wrote down a license plate number – something I have the habit of doing when a situation seems suspicious.
In Qui à tué Roger Ackroyd?, Bayard analyzes Agatha Christie’s famous detective novel The Murder of Roger Ackroyd (1926). The literary critic disagrees with detective Hercule Poirot’s conclusion: Ackroyd’s murderer is not the narrator, James Sheppard, as Poirot would have it. It’s a delirious interpretation, ‘consistant à rechercher minutieusement des indices, à interpréter des faits et à organiser nos déductions en une construction d’ensemble harmonieuse’.
The car with license plate number XHD 558 is unknown to me. I can’t recall what I saw that urged me to write it down, nor the time or location when I saw it.
Bayard, P. Qui a tué Roger Ackroyd? Paris: Minuit, 2008.

Recreational airfield at Grimbergen, webcam footage.
09:10:00The frame shows the first movement on the terrain. The gate has been opened, the barrier lowered. A black car is in the back. In the forefront, aviation signs on the ground: a yellow cross on a surface painted red; an arrow in a 90° angular shape; two circles connected by a line; a T-shaped line.
09:20:00Two men talking, each one on one side of the barrier. The man on the side of the airstrip has two dogs with him. The aviation signs have changed: the arrow is gone; the horizontal bar of the T-symbol has moved to the other side of the vertical line; one yellow line that made up the cross on the red surface is gone, leaving one yellow diagonal line.
10:09:01A small white aircraft (the two men and the dogs are gone).
10:20:01The aircraft in the same position, with what seems to be an open roof.
10:40:00Aircraft leaving the gas station where it was before.
11:10:01A white car at the gas station, where previously the aircraft was stationed; a silhouette of a man, perhaps.
11:30:01White car gone.
11:50:01Small white aircraft at the gas station; man in red jacket next to the aircraft. Not clear if it is the same aircraft seen in frame 10:09:01.
12:10:01Aircraft appears to be heading for take-off.
12:20:01Aircraft gone.
12:40:01White dots on the grass that appear to be birds.
14:10:00First precipitation: snow, visibility lessens.
14:20:00More snow, wind is stronger; someone has replaced the yellow stripe so that, again, a yellow cross is formed on the red background.
15:10:00The grass and the concrete get increasingly white. No aircrafts, vehicles or persons can be discerned. The aviation signs beneath the thin-layered snow are still visible, and unaltered.
Every so often architects ask me to photograph projects of theirs under a blanket of snow. Snow-days are rare around here. In an attempt to avoid a futile drive along roads in winter conditions, I check webcams near the project-to-be-photographed before setting out.
Webcam Grimbergen, meteobelgie.be: https://www.meteobelgie.be/waarnemingen/belgie/webcam/272/grimbergen
http://www.rvg.be

Summer 2019, between the swingset and the mesh greenhouse, astrophotographer Angelo Van Daele closes the observatory. The wheels roll smoothly across the rails embedded within a concrete slab. His former observatory is now a chicken coop. His neighbour’s trees need pruning. The camera mounted on the exterior of the shed allows him to see the instrument from inside the house.
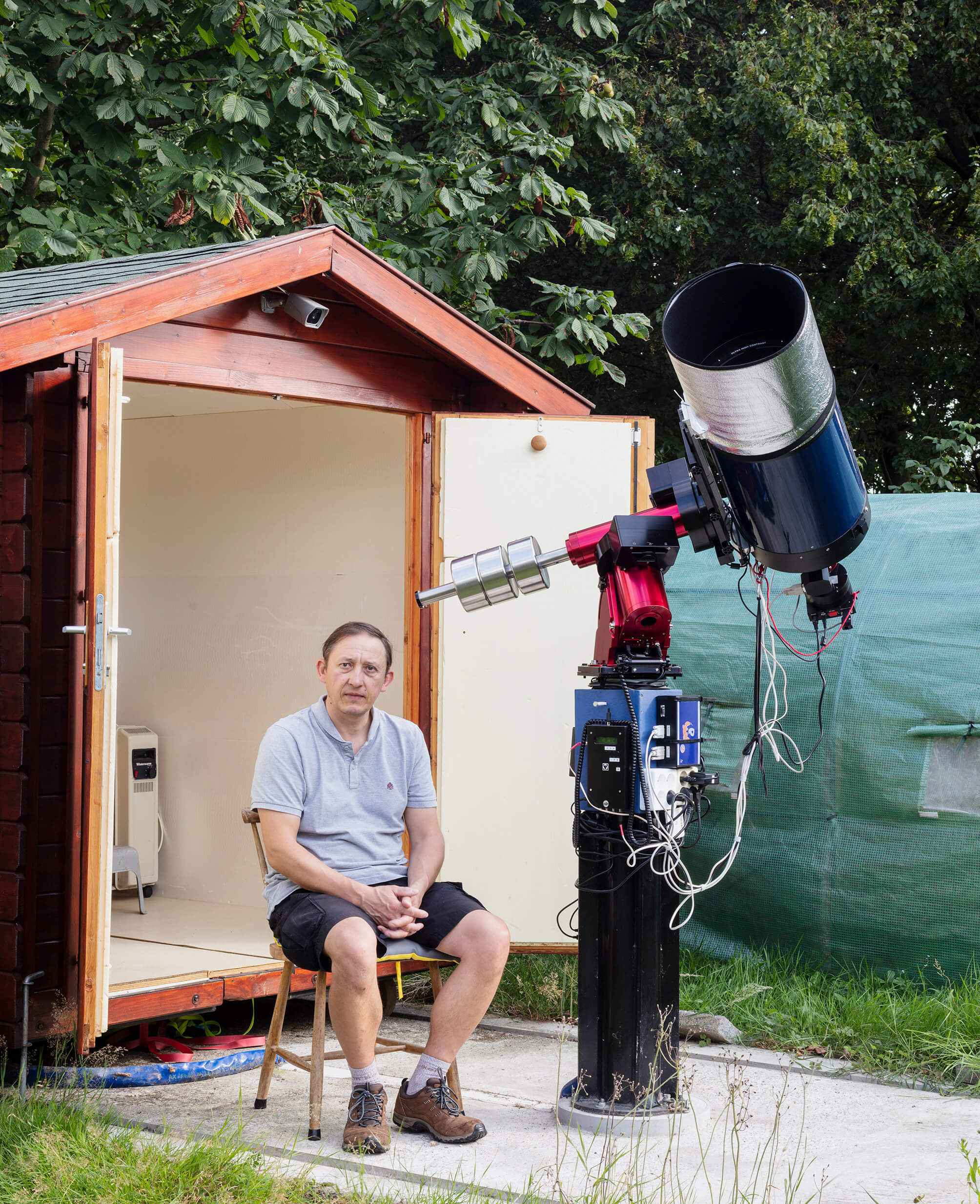

As an architectural structure, the pier is fundamental in observational astronomy: it can be found in the backyards of amateur observatories, as well as in professional ones. This column is a quintessential part of the physical interventions that are necessary to distinguish noise from valuable data. The pier disjoints the telescope from the observer, from the observatory and from the surroundings. Tremors of passing cars, the astronomer’s footsteps and coughs, the neighbour’s soundsystem: they could result in an agitated telescope. A falling mug would cause the instrument to shift lightyears away from its target.
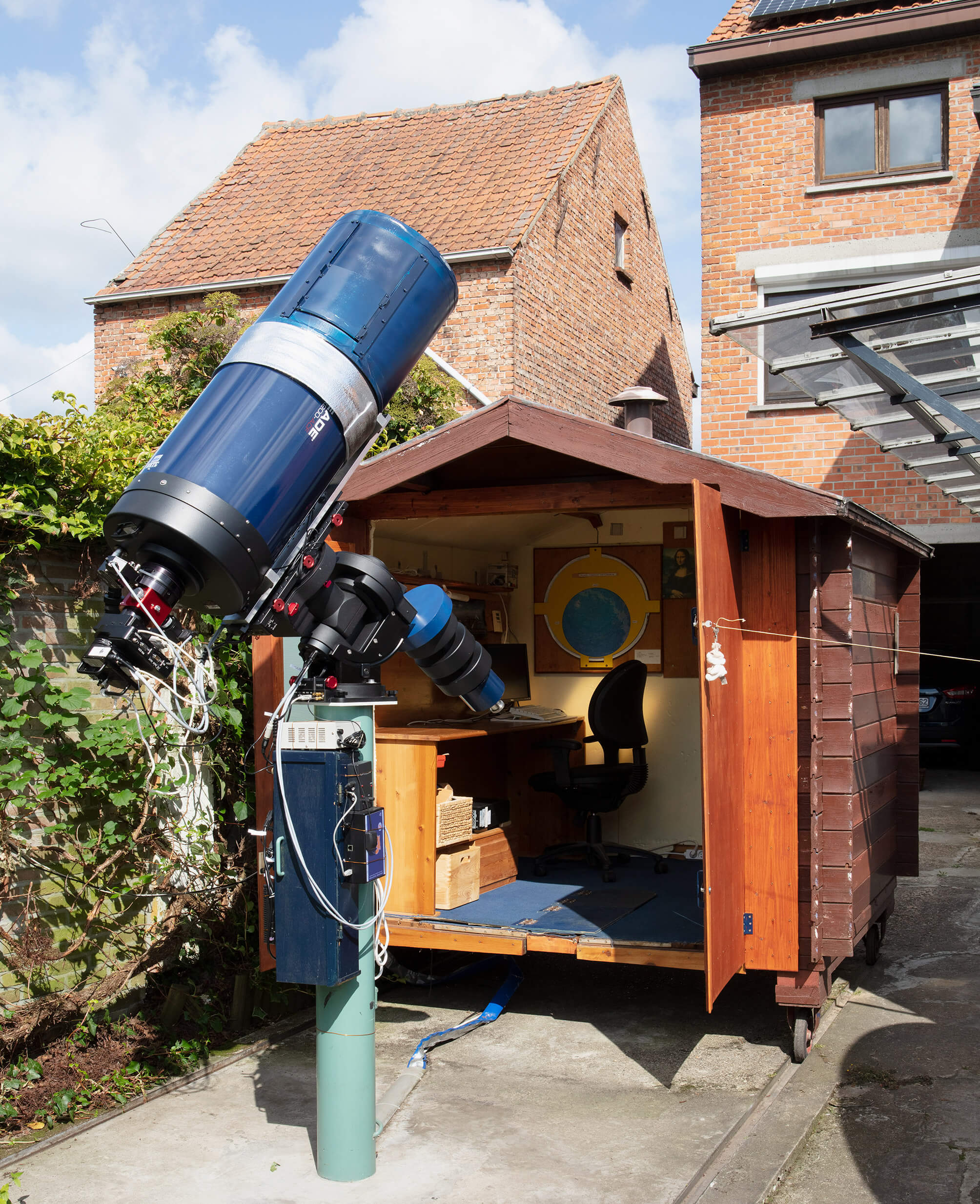
In August 2019, I visited Chris De Pauw, an astrophotographer, at home. He showed me his private observatory. As we were both waiting for clouds to obscure the sun and get softer light for the photograph, he told me about the rolling shed, its advantages and the modifications he was planning on.
On closing the observatory – by rolling the shed over the instrument – he manoeuvred the instrument into its ‘park’-position: an azimuth of 160 degrees and an elevation of 8 degrees above the horizon. The shed’s doors and hinges barely cleared the telescope.


It’s 21:49 on Tuesday May 4th 2021. I’m sifting through the folders of a back-up drive. When I reach Archief2A/2017/wigny donder, the subfolder contains 103 items (97 DNG-files, 1 JPEG-file and 5 PSD-files). The photographs are all very similar. They show the silhouette of the same tree and hills, the red light of the telecommunications mast on the left and the orange glow of the street’s sodium lights. The thunderstorm moves from right to left. _44A3920 is the only exposure (10 seconds) that recorded lightning bolts.
I looked up heat lightning, also known as silent lightning, summer lightning, or dry lightning, which is simply cloud-to-ground lightning that occurs very far away, with thunder that dissipates before it reaches the observer. On YouTube I watched: Top 10 Dangerous Lightning Strikes Thunder recorded on Camera (HIGH VOLTAGE!!) followed by Lightning Strikes at the 2019 U.S. Women’s Open. It’s 22:07, I am doubtful at first but become convinced I can hear thunder afar.

In Boarhunt, close to Winchester (UK), the fort houses the Royal Armouries’ artillery collection. It contains parts of the ‘Project Babylon’ space gun, the two part bronze Dardanelles Gun and a collection of French field guns, captured in Waterloo. On the lawn to the South of the fort two neat piles of fifteen1 36” shells flank a Mallet’s Mortar. Manufactured in 1857, the mortar remains unfired up to this day.2 In 1873, its inventor – the engineer and geophysicist Robert Mallet – publishes his translation of Luigi Palmieri’s Incendio Vesuviano. Before giving a lengthy account of his take on the present state of vulcanicity, he briefly introduces the famous Italian vulcanologist’s report: ‘The following Memoir of Signor Palmieri on the eruption of Vesuvius in April of this year (1872), brief as it is, embraces two distinct subjects, viz., his narrative as an eye-witness of the actual events of the eruption as they occurred upon the cone and slopes of the mountain, and his observations as to pulses emanating from its interior, as indicated by his Seismograph, and as to the electric conditions of the overhanging cloud of smoke (so called) and ashes, as indicated by his bifilar electrometer, both established at the Observatory.’
O
O OOO
OOO OOOOOOO
In the outskirts of East of London, along Repository road in Woolwich, the only other mortar of this type is installed. This particular one fired nineteen shells on three occasions. Each time resulting in a damaged mortar.
Screenshot taken from AbeBooks, where the first edition of The Eruption of Vesuvius in 1872 with Notes, and an Introductory Sketch on the Present State of Knowledge of Terrestrial Vulcanicity, the Cosmical Nature and Relations of Volcanoes and Earthquakes is listed for 1895,00 USD. https://www.abebooks.com/first-edition/Eruption-Vesuvius-1872.with-Notes-Introductory-Sketch/439314424/bd
Project Gutenberg’s The Eruption of Vesuvius in 1872, by Luigi Palmieri (translated by Mallet) can be found at: https://www.gutenberg.org/files/33483/33483-h/33483-h.htm

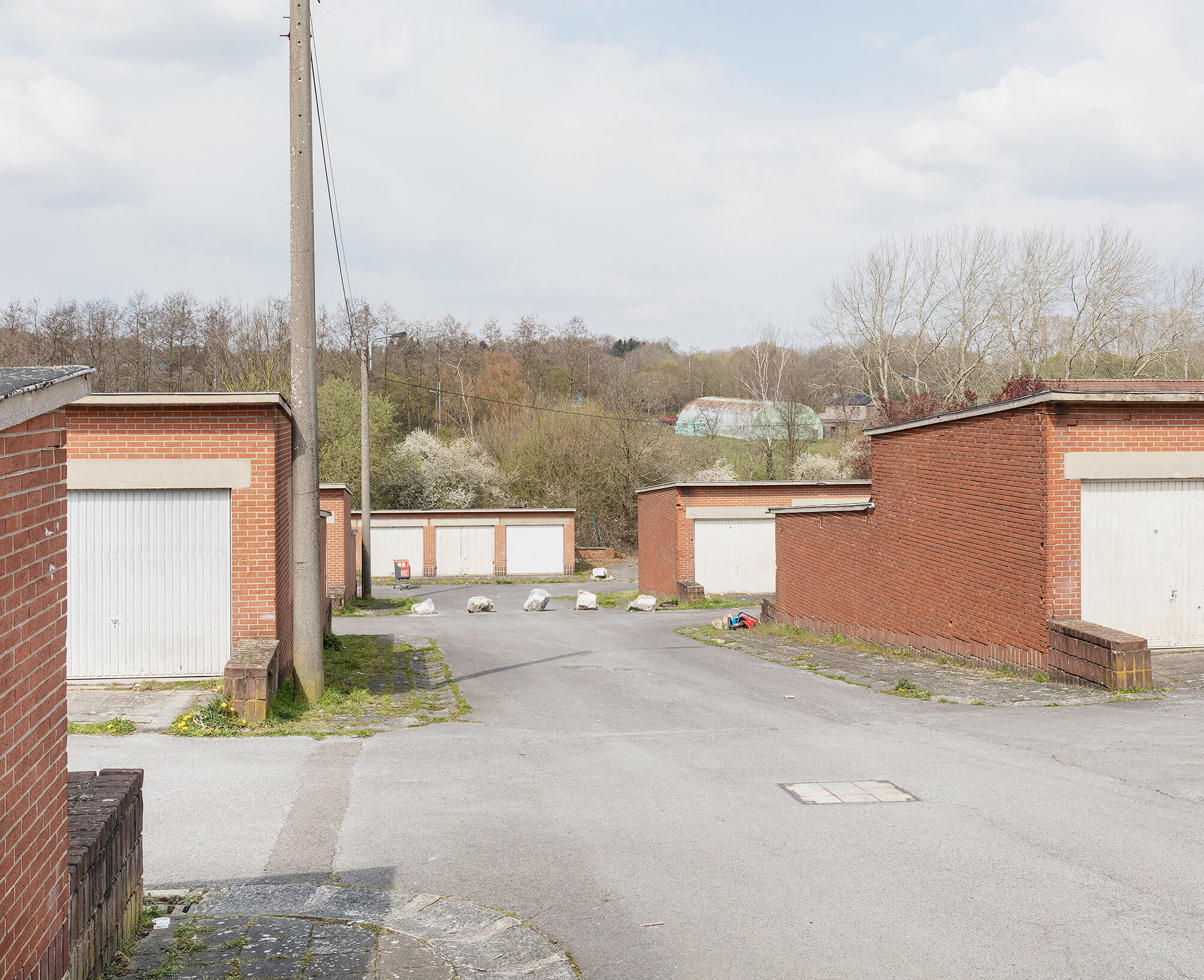
Seven very similar and rudimentary buildings take in a trapezoid plot of land in Gilly. They are located between the school on the Rue Circulaire and the houses along the Rue de l’Abbaye. The structures are built of orange brick, concrete structural elements, whitish steel gates and roofing. Every garage has its own number, hand-painted in white on the concrete lintel above each gate. In summer the roofing gets hot and soft.

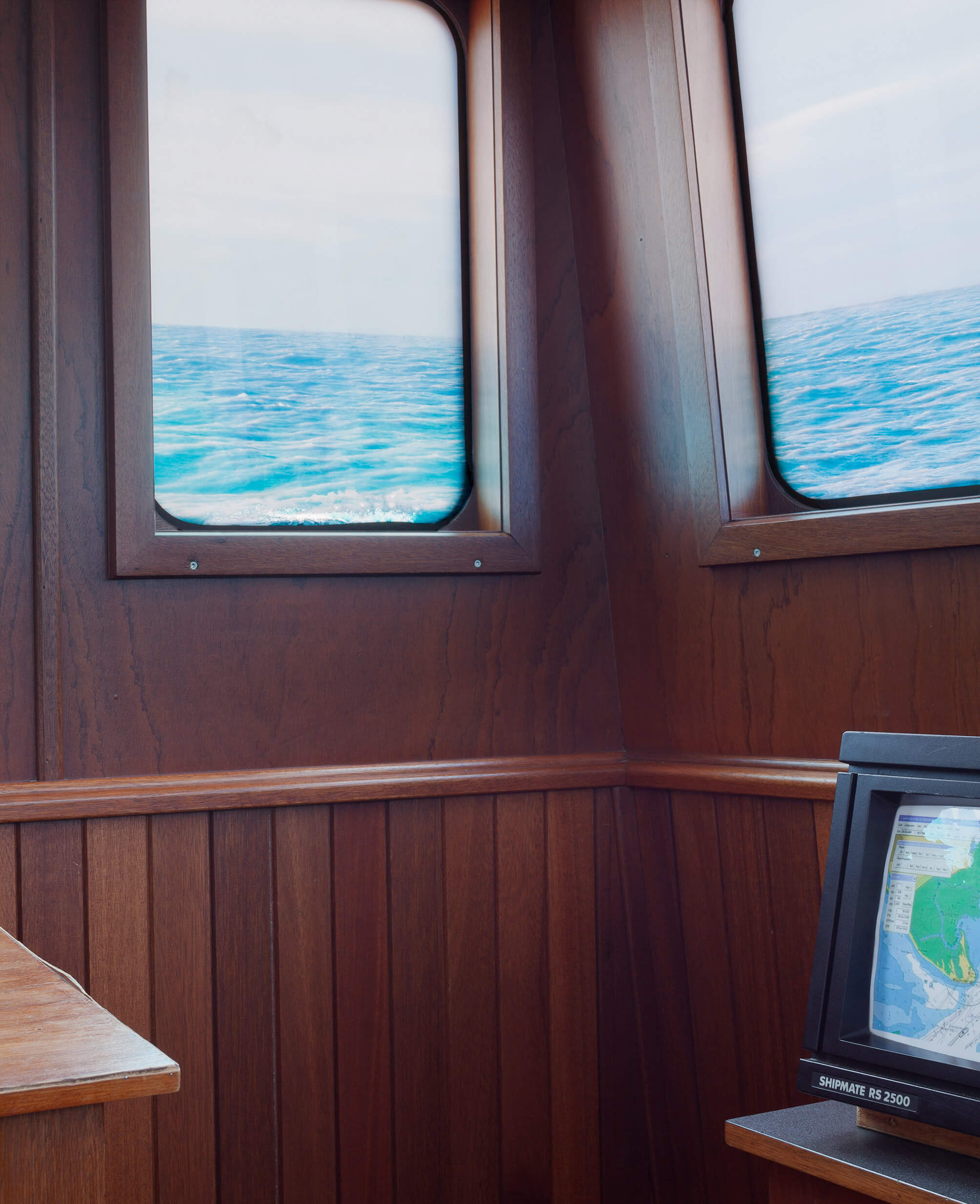
The GPS-plotter displays the ship near Keyhaven Lake, indefinitely. The sea appears calm, the horizon is level from one perspective.

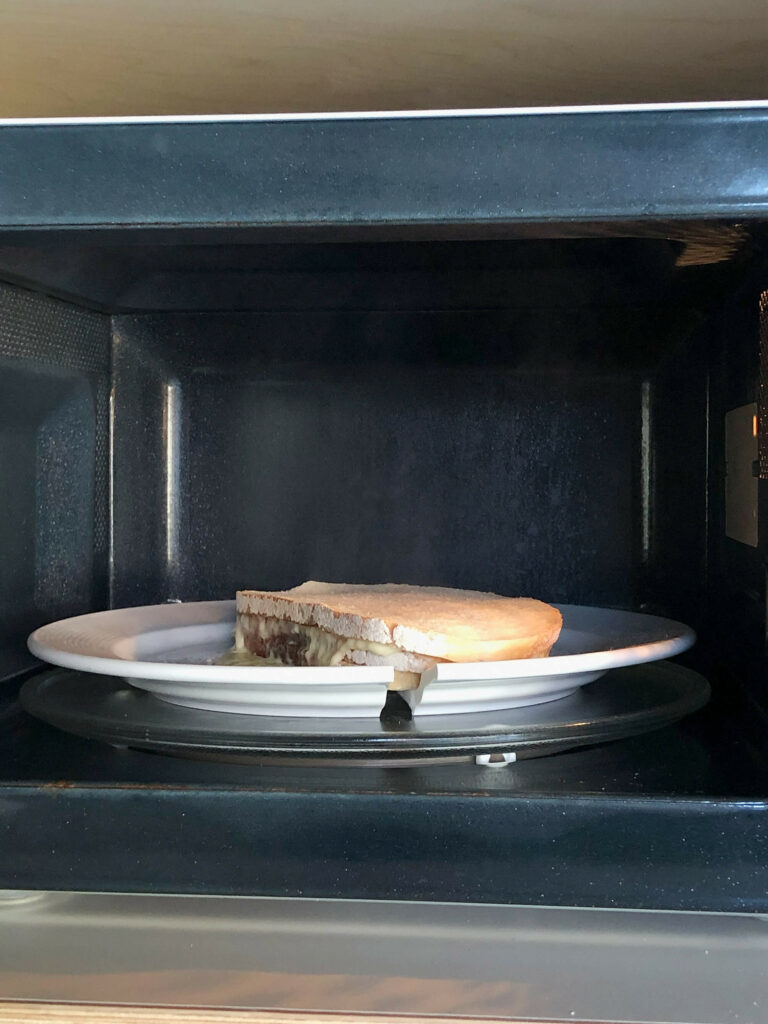
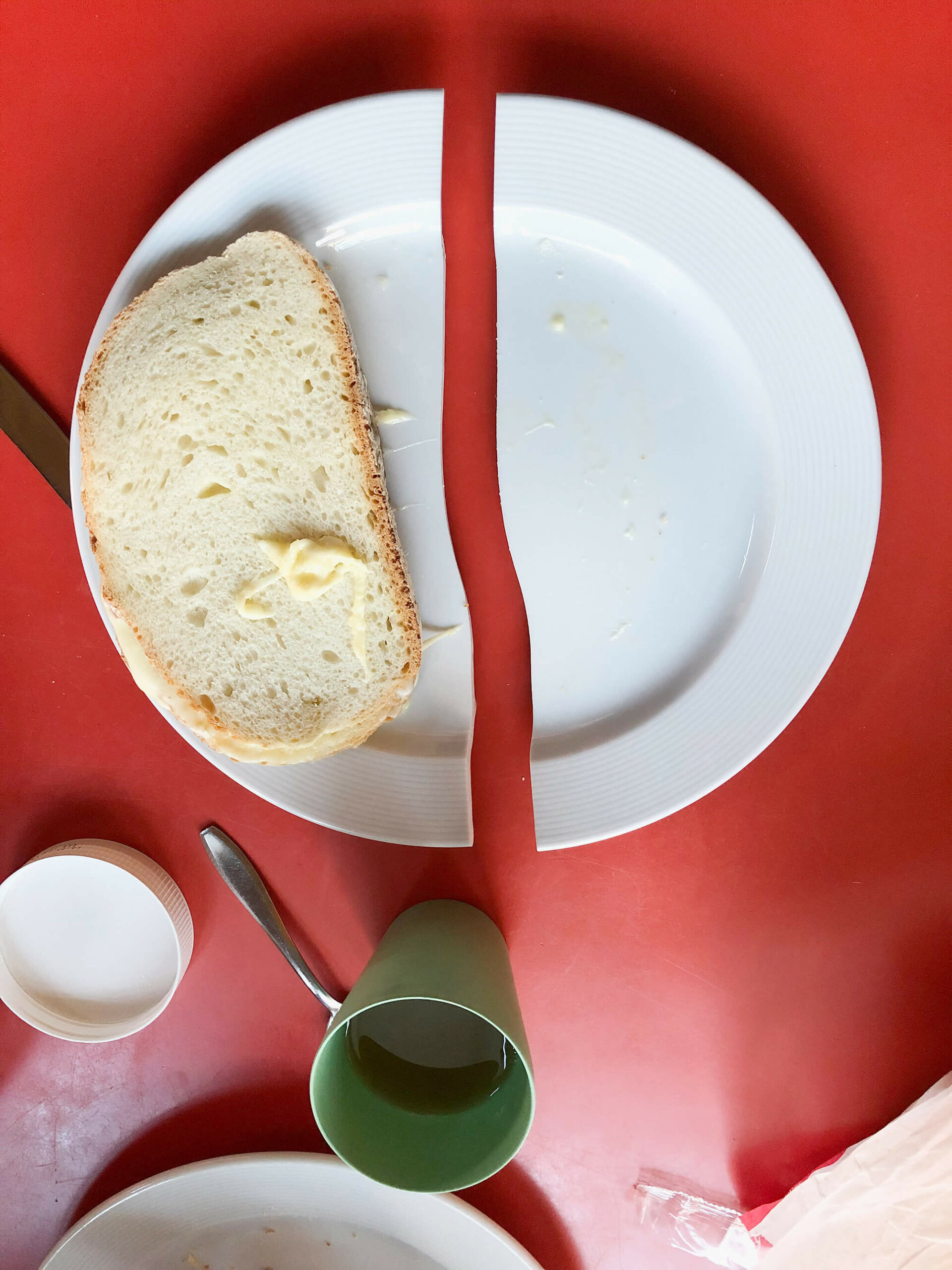
Most mornings I eat three slices of bread. I stack them. Between the highest slice and the one in the middle I put a slice of cheese (young Gouda). I put the whole in the microwave1 for 1 minute and 50 seconds. The result is what I like to call a smelteram2.
On the morning of my thirty-second birthday the plate broke in half during heating.

A contraction of smelten (Dutch for melting) and boterham (Dutch for a slice of bread).

Until recently, for as long as I could remember, the packaging of Tabasco® Pepper Sauce had been unchanged. On the front of the packaging, there is a photograph of a bottle of Tabasco®, scale 1:1, against an orange background.As far as packaged goods go, this is a highly idiosyncratic and quirky example.
The background colour approximates the colour of the liquid inside the bottle, resulting in as good as no contrast. Moreover, as the image of the bottle is scale 1:1, the packaging becomes kind of unnecessary and superfluous, also because the life-sized image of the bottle is the only way information is given to the customer: there are no additional slogans, no repetition of the brand name, no props and no decor. The image of the bottle advertises the bottle. It seems to add nothing the bottle could not do by its own (like a bottle of wine does).
What makes the packaging truly stand out, however, is the fact that the image of the bottle is not positioned vertically, but is slightly askew. It seems to be the result of a design error, and has an amateur feel to it. The decision to keep it as such and not correct it up until today, is, however, a stroke of genius. The non-vertical positioning alters the relation of the image of the bottle to the bottle inside: as the box is standing on a shelf, the tilted image of the bottle undermines its representational superfluousness.

At the State Archive in Kortrijk, I am leafing through a 1955 photo album of the construction of the provisional church in Lokeren by the famous furniture company Kunstwerkstede De Coene. Gigantic wooden, prefabricated beams structure the building. It is cold. An old man in a grey suit shuffles between the racks to look up the date of birth of his great great grandmother. Snow covers the unfinished provisional roof. A bus passes, I reckon, through the pouring rain.

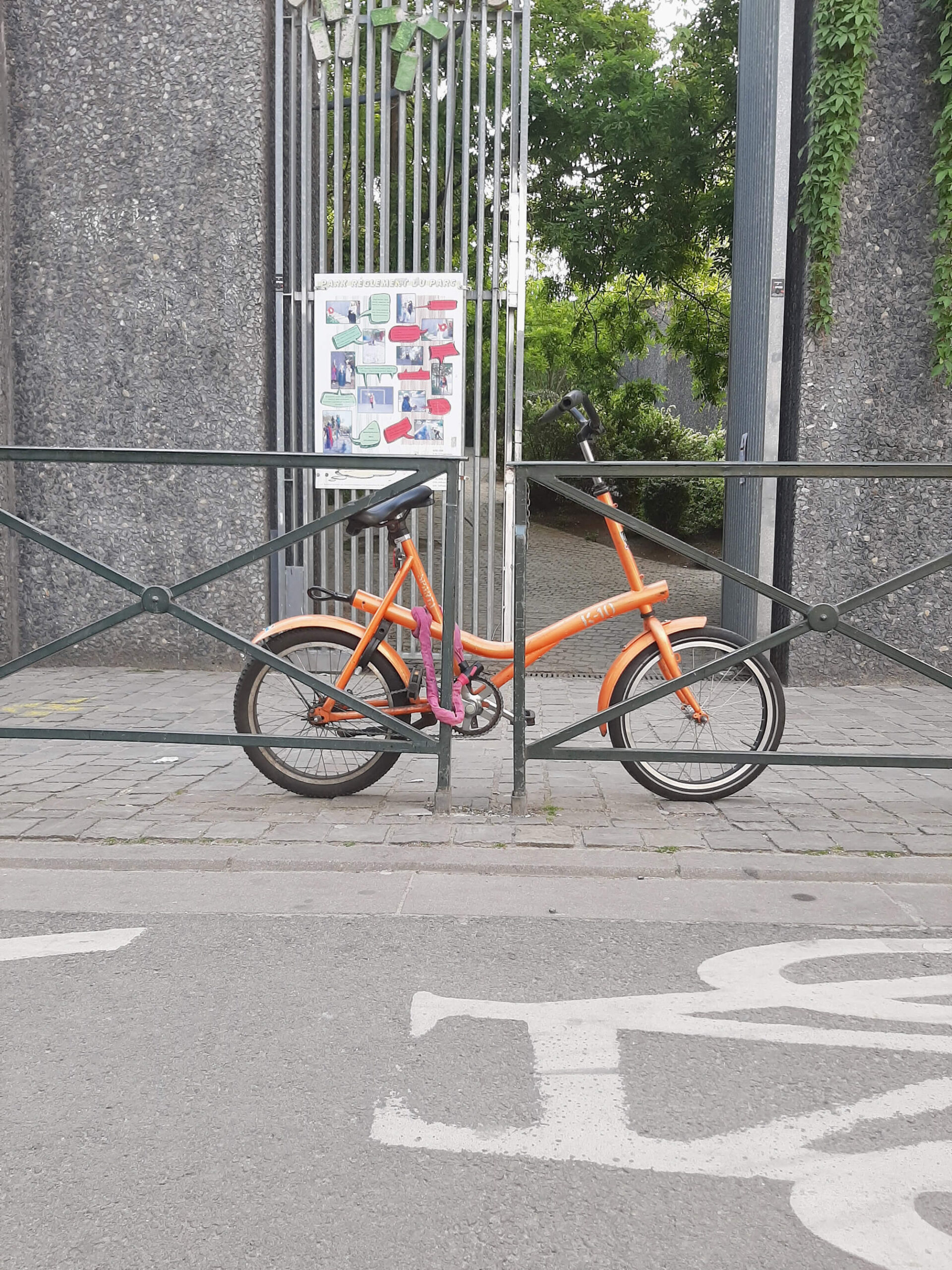
John from Middelburg offers a K-10 without a loop at the back on marktplaats.nl. His K-10 does have a front light, which strangely never seems to be mounted in the front of the long tube of the frame. The asking price is 75 euros, bids may start from 50 euros.
Lars Kwakkenbos lives and works in Brussels and Ghent (B). He teaches at KASK & Conservatorium in Ghent, where he is currently working on the research project ‘On Instructing Photography’ (2023-2024), together with Michiel and Arnout De Cleene.

This bike regularly pops up on the streets of the Brussels neighbourhood where I live. On 4 June 2021, it stands in Rue Verte, in front of the entrance to the Reine Verte Park. The park is built on one of the steepest slopes in Brussels. That condition required a clever park design, in which you can hang out or walk from Rue Verte to Rue des Palais, up, or vice versa, down. The park is well cared for by city services.
The bike is an orange Sparta K-10. It has a remarkably low entry and high handlebars. As a result, it seems to be a comfortable bike, albeit one whose body posture while cycling is not geared to the gradient of our neighbourhood, in which it usually stands. Moreover, it has no gears and the saddle is very slanted.
Lars Kwakkenbos lives and works in Brussels and Ghent (B). He teaches at KASK & Conservatorium in Ghent, where he is currently working on the research project ‘On Instructing Photography’ (2023-2024), together with Michiel and Arnout De Cleene.
