What constitutes a ‘document’ and how does it function?
According to the Oxford English Dictionary, the etymological origin is the Latin ‘documentum’, meaning ‘lesson, proof, instance, specimen’. As a verb, it is ‘to prove or support (something) by documentary evidence’, and ‘to provide with documents’. The online version of the OED includes a draft addition, whereby a document (as a noun) is ‘a collection of data in digital form that is considered a single item and typically has a unique filename by which it can be stored, retrieved, or transmitted (as a file, a spreadsheet, or a graphic)’. The current use of the noun ‘document’ is defined as ‘something written, inscribed, etc., which furnishes evidence or information upon any subject, as a manuscript, title-deed, tomb-stone, coin, picture, etc.’ (emphasis added).
Both ‘something’ and that first ‘etc.’ leave ample room for discussion. A document doubts whether it functions as something unique, or as something reproducible. A passport is a document, but a flyer equally so. Moreover, there is a circular reasoning: to document is ‘to provide with documents’. Defining (the functioning of) a document most likely involves ideas of communication, information, evidence, inscriptions, and implies notions of objectivity and neutrality – but the document is neither reducible to one of them, nor is it equal to their sum. It is hard to pinpoint it, as it disperses into and is affected by other fields: it is intrinsically tied to the history of media and to important currents in literature, photography and art; it is linked to epistemic and power structures. However ubiquitous it is, as an often tangible thing in our environment, and as a concept, a document deranges.
the-documents.org continuously gathers documents and provides them with a short textual description, explanation,
or digression, written by multiple authors. In Paper Knowledge, Lisa Gitelman paraphrases ‘documentalist’ Suzanne Briet, stating that ‘an antelope running wild would not be a document, but an antelope taken into a zoo would be one, presumably because it would then be framed – or reframed – as an example, specimen, or instance’. The gathered files are all documents – if they weren’t before publication, they now are. That is what the-documents.org, irreversibly, does. It is a zoo turning an antelope into an ‘antelope’.
As you made your way through the collection,
the-documents.org tracked the entries you viewed.
It documented your path through the website.
As such, the time spent on the-documents.org turned
into this – a new document.
This document was compiled by ____ on 10.03.2022 12:37, printed on ____ and contains 15 documents on _ pages.
(https://the-documents.org/log/10-03-2022-3903/)
the-documents.org is a project created and edited by De Cleene De Cleene; design & development by atelier Haegeman Temmerman.
the-documents.org has been online since 23.05.2021.
- De Cleene De Cleene is Michiel De Cleene and Arnout De Cleene. Together they form a research group that focusses on novel ways of approaching the everyday, by artistic means and from a cultural and critical perspective.
www.decleenedecleene.be / info@decleenedecleene.be - This project was made possible with the support of the Flemish Government and KASK & Conservatorium, the school of arts of HOGENT and Howest. It is part of the research project Documenting Objects, financed by the HOGENT Arts Research Fund.
- Briet, S. Qu’est-ce que la documentation? Paris: Edit, 1951.
- Gitelman, L. Paper Knowledge. Toward a Media History of Documents.
Durham/ London: Duke University Press, 2014. - Oxford English Dictionary Online. Accessed on 13.05.2021.
At the nuclear waste processing facility. While the photographer and the head of the communication department are making their way from the processing building to the temporary storage building, they walk past the central chimney.
‘On the highest of the accessible levels of the chimney, operators were finding small steel rings. They gathered them, but soon noticed that new rings were added. At a certain point at a rate of one ring a day.
[…]
It took them some time to realize what they were, so they started collecting them by slipping them onto a piece of rope. By now the rings on the rope span about this distance [spreads his arms to indicate a distance of about 1.2m].
[…]
They turned out to be rings that came from pigeon’s legs.
[…]
On top of our chimney resides a peregrine falcon.
[…]
I was told pigeon fanciers have a tendency to give a peregrine falcon – or any other bird of prey in their area – a hand at disappearing, but this one took up residency in the internal perimeter, where – as you know – access is severely restricted.’
First published in: De Cleene, M. Reference Guide. Amsterdam: Roma Publications, 2019

‘ORIGINAL. Rire de tout ce qui est original, le haïr, le bafouer, et l’exterminer si l’on peut.’
[‘ORIGINAL. Laugh with everything that’s original, hate it, scold it, exterminate it if you can.’]
Flaubert. Bouvard et Pécuchet (présenté par Raymond Queneau). Paris: Livre de poche, 1959 (with p. 232-233: dried leaf of a ginkgo tree, and p. 324-325: dried leaf of a birch tree), p. 429 [2,00 EUR, Librairie Vic-sur-Cère, August 2021].

It snows on December 19, but the situation changes on the 22nd with the arrival of an Atlantic low-pressure area, bringing masses of hot and humid air. Thaw follows.
And then, it snows again on December 26 and 27, before the arrival of a new warm front on the same day. A significant and brutal rise in temperature ensues: at Lac Noir, at 920 m, the temperature shoots up from 0,3 °C on December 27 at 7 AM to 7,4 ° C on the 28th at 9 PM.

The building is almost finished. One apartment is still up for sale, on the top floor. The contractor is finishing up. There’s a long list of comments and deficiencies that need to be addressed before the building can be handed over definitively to the owner. The elevator’s walls are protected by styrofoam to prevent squares, levels, measures, drills, air compressors, chairs, bird cages, etc. from making scratches on the brand new wooden panelling.
In 1932 Brassaï began taking photographs of graffiti scratched into walls of Parisian buildings. On his long walks he was often accompanied by the author Raymond Queneau, who lived in the same building but on a different floor. Brassaï published a small collection of the photographs in Minotaure, illustrating an article titled ‘Du mur des cavernes au mur d’usine’ [‘From cave wall to factory wall’].

Cathedral glass, or Flemish glass, lets light through, but distorts visibility. It can show something or someone is present behind it, but not in detail. Often used in front doors, it marks the opaque edge between the private and the public sphere, laying bare their presence, without disclosing their contents.
A blue hand, or a spider (Cyriopagopus lividus), traces the cracks that testify to the fact that the jammed door had to be closed with force. The hinges need oiling. Cobalt blue tarantulas are said to be extremely defensive.


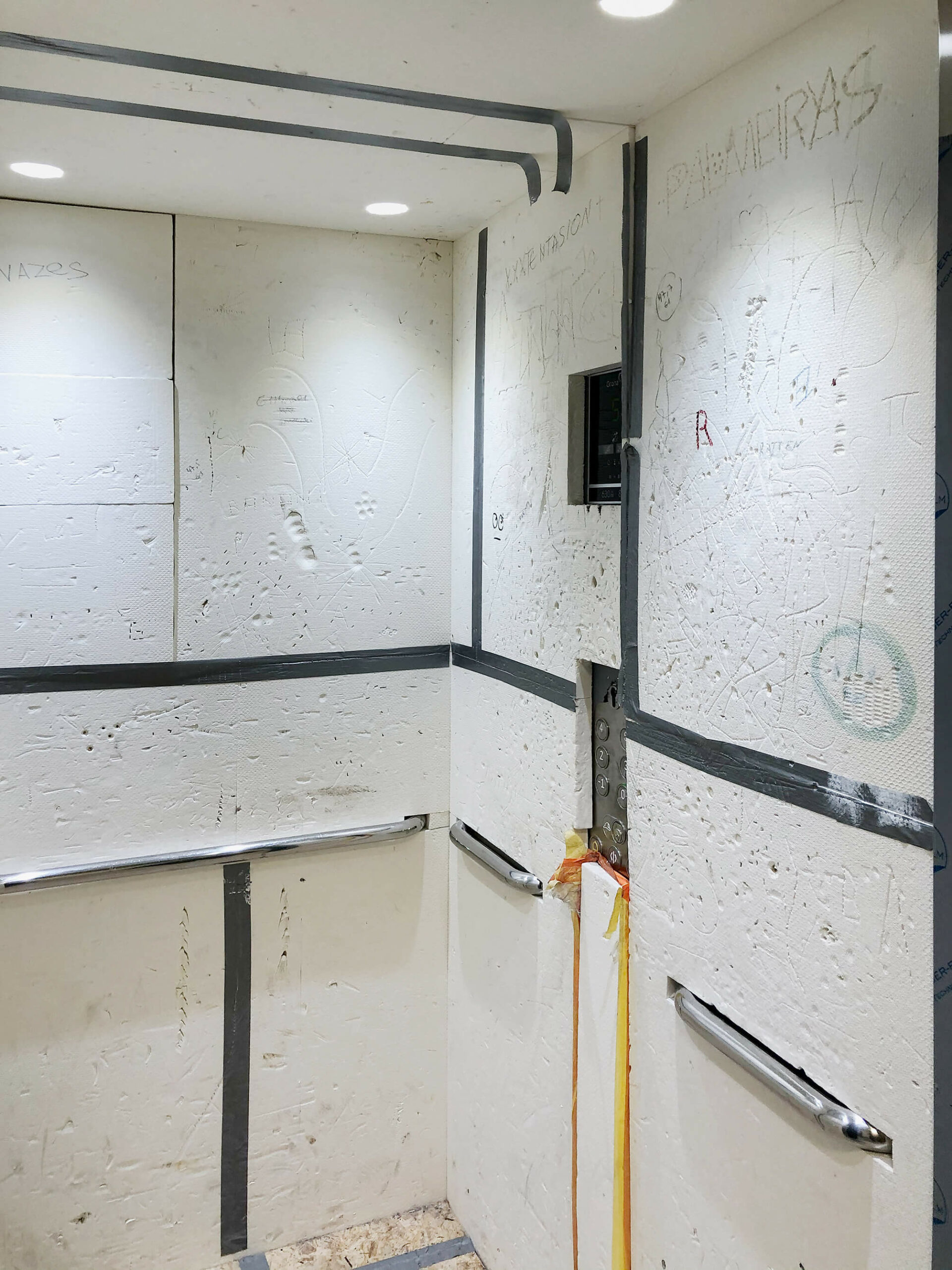
A cigar box, standing at the back of a shelf next to the heating installation, with in it silex-like stones with what seem to be traces of prehistoric usage.
In the garage, there were papers (the archive of O. Clemminck) and objects (stones, tiles) left to us by a man who had worked at the city archive. He was an acclaimed expert on our village’s history.1
A recent study by professor Philippe Crombé at Ghent University states that during the last Ice Age, in the region where I grew up, there was once a great lake, with, at the shores, proven presence of prehistoric man. As a kid, we dug up shells with a toothbrush, and set a perimeter with plastic tape. The former presence of a tavern where my parents now live, and the restaurant which still serves seafood at the other side of the road, prevented accurate dating.

At the copyshop, on a shelf above photocopier 8, the lid of a box of paper serves as the container for ‘forgotten originals’.1
The book being copied: Didi-Huberman, G. La ressemblance par contact. Archéologie, anachronisme et modernité de l’empreinte. Paris: Les Editions de Minuit, 2008.

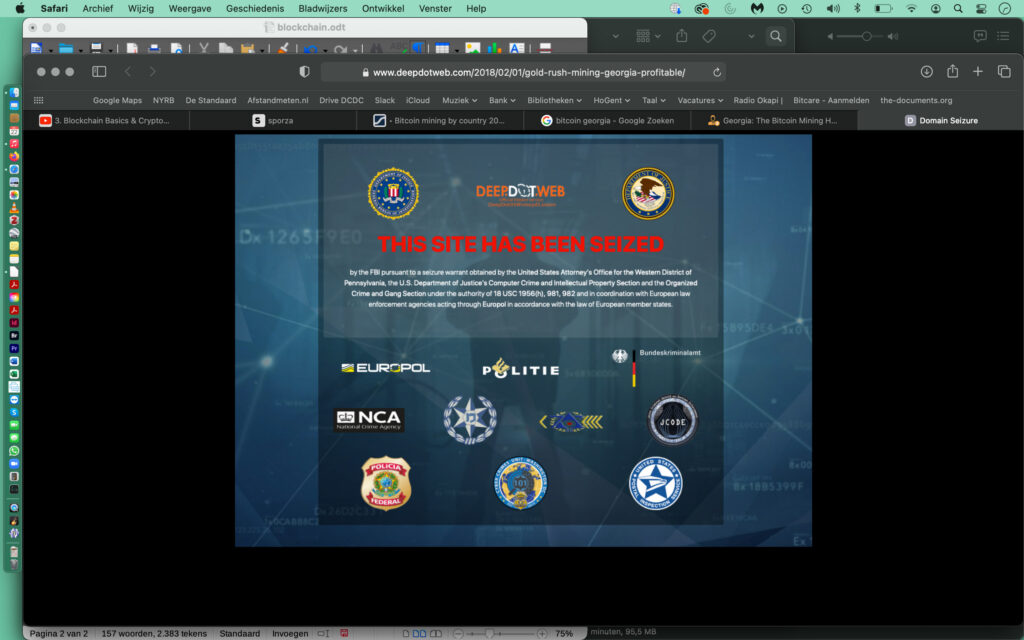
Conducting research into the effects on energy consumption of blockchain-based applications such as bitcoin, I was triggered by the fact that many of the facilities making blockchain-mining1 possible are located in Georgia. Low energy prices and a relaxed taxation policy are said to be among the reasons why companies such as Bitfury locate their plants there.
After a three-day hike in the Caucasus Mountains, on the Georgian side of the border with Chechnya, we are invited to pitch our tent in the garden of Murati, a local farmer in a small mountain village. We are overwhelmed by the scenery and Murati’s hospitality. Many of the villages, thrown on the mountain flanks, have tower-like structures of some twenty meters high, making them all look fortified. They have no windows or doors on the ground floor.2
Murati invites us into his house to drink warm milk with his family and brings us cheese-filled bread. One of us speaks Russian. He inspects our backpacks, headlights and drinking bags. He tells us a 500 kilogram pig of his did not return to the house that night. The family is saddened.
In the evening, we see him taking his granddaughter by the hand. They walk to the highest point of the gravel road in front of his house and together watch the last light of the day fall on the snow-covered triangular peak of one of the Caucasus’ highest mountains.
I’m mistrusting my memory and look the passage up in the journal we kept. The village is called Zagar. The mountain is Mount Tetnuldi. The granddaughter’s name is Anna.
When I click through to one of the websites promising information on Georgia’s blockchain economy, I happen to stumble on a dark web-related website and access is denied.3
‘Mining’ is what is being done when data – a transaction – has to be added to the blockchain (which, in itself, is the sum of all previous transactions, added to each other as data). To do this, computers have to solve a complex mathematical puzzle, which is crucial for the trustworthiness of the system, but for which loads of energy is needed. Criticism on the effects of blockchain-mining is growing, as it has a gruesome effect on resources. In 2018, Andrew North writes, Bitfury used 28 million kilowatt-hours of electricity per month, equalling the consumption of 120,000 Georgian households.


A mostly empty book designed to collect cigar bands. The bands are glued to the paper at their left side, so the information on the backside, explaining the image and referring to the series it belongs to and the number of different labels the series contains, can be looked up. The book has complete and incomplete series on Christopher Columbus (complete), tanks (incomplete), the origins of civilization (complete), Ancient cultures (incomplete), fashion (complete), South-American sculptures (complete), Ancient columns (incomplete), Nobel Prize Winners (incomplete), an unclarified series of seven men, most of whom are ‘prof.’ or ‘dr.’(complete / incomplete), design plates (incomplete), famous Belgians (complete / incomplete), statesmen (incomplete) and football players (incomplete). The first page in the book is used to present two series. The left column presents the Egyptian dynasty (incomplete). The middle and right column present a series of bands by the brand Jubilé on the history of energy in telling scenes and pieces of machinery.
Series: Energy
Middle column, top to bottom:
- The writing telegraph. Hughes
- Experiment with a sulphur globe. William Gilbert
- Primitive telephone. Philipp Reis
- Wireless telegraph.1 Guglielo [sic] Marconi
- The arc of Volta. Sir Humphry Davy
- Fire in the wagon. Thomas Alva Edison
- Experiments with lightning. Benjamin Franklin
- Cathode for creating X-Rays. Wilhelm Röntgen
- Rotating magnetic field. Galileo Ferraris
Right column, top to bottom:
- Electric discharge. William Watt
- Magnetic telephone. Antonio Meucci
- Muscles reacting to electricity. Luigi Galvani
- Voltaic pile. Alessandro Volta
- Oscillating circuit. Guglielo [sic] Marconi
- Development of the telephone. Graham Bell
- Telephone, beginning of the 20th century
- Next to his wireless telegraph. Guglielo [sic] Marconi
- Invention of the incandescent light bulb. Thomas Alva Edison
- Morse’s telegraph. Samuel Morse
The series is incomplete.2
The scene shows a man standing at a desk, sticking out his hand to an officer in a window that reads, in mirror writing: Customs.
On eBay a complete series is advertised (15 EUR), with a lo-res picture of the whole collection, including the five bands missing in my grandfather’s collection. The information on the back, however, is not given. It leads to a highly speculative history of energy.
A man in a gown watching a T-shaped object.
A child in a cellar, sitting on a stool at a table with gray objects.
A soldier kneeling beside a child, in front of a train, and in front of a boat.
A low table with a giant cartwheel of sorts and a box.
A vertical object with what seems to be a bell on top.

Article 75 of the Royal Decree containing general regulations for road traffic and the use of public roads, published in Het Belgisch Staatsblad on 9 December 1975, lists the rules for longitudinal markings indicating the edge of the roadway.
According to 75.1, there are two types of markings that indicate the actual edge of the roadway: a white, continuous stripe and a yellow interrupted line. The former is mainly used to make the edge of the roadway more visible; the latter indicates that parking along it is prohibited.
In 75.2, the decree focuses on markings that indicate the imaginary edge of the roadway. Only a broad, white, continuous stripe is permitted for this purpose. The part of the public road on the other side of this line is reserved for standing still and parking, except on motorways and expressways.
https://wegcode.be/wetteksten/secties/kb/wegcode/262-art75

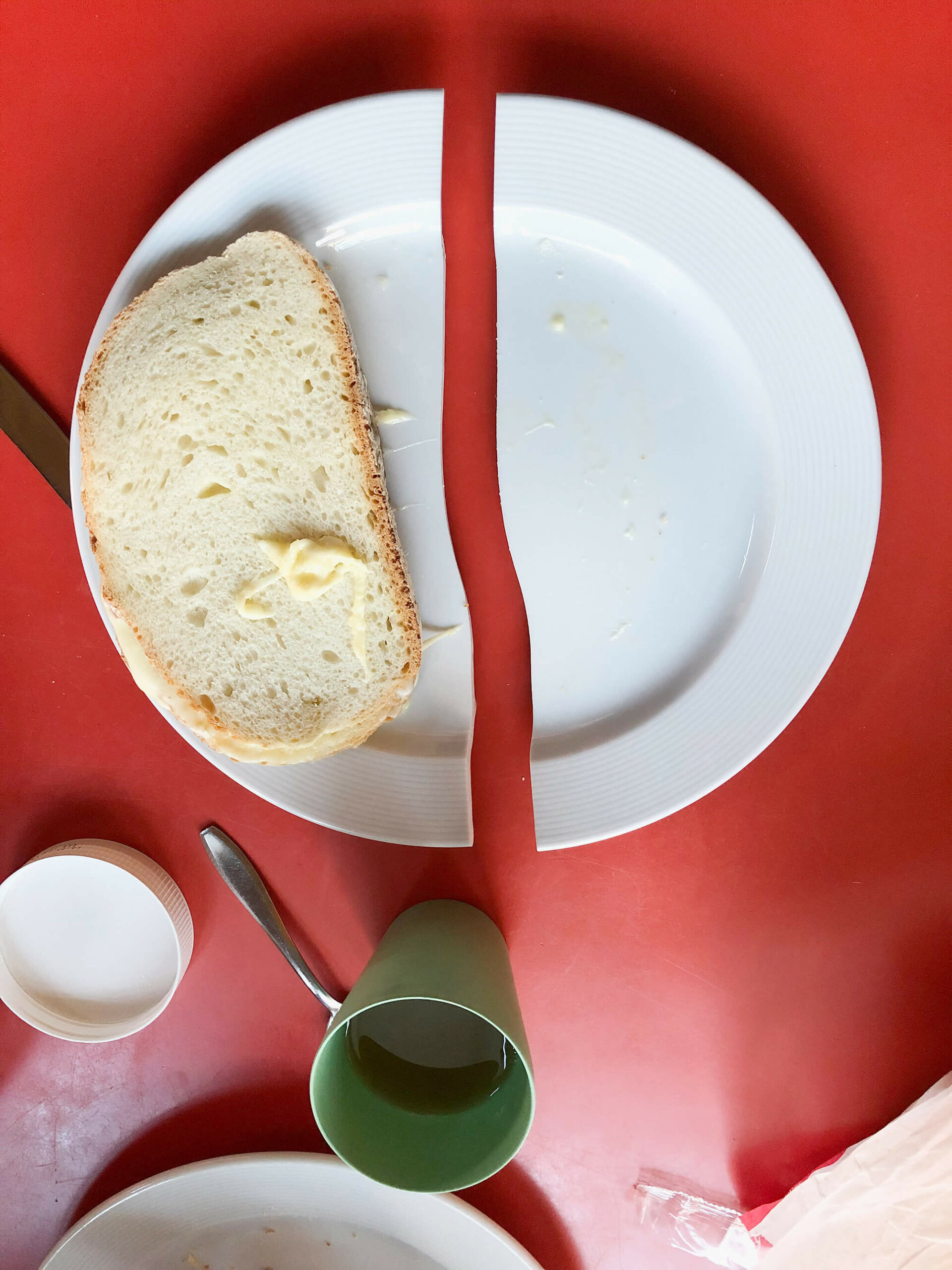
Most mornings I eat three slices of bread. I stack them. Between the highest slice and the one in the middle I put a slice of cheese (young Gouda). I put the whole in the microwave1 for 1 minute and 50 seconds. The result is what I like to call a smelteram2.
On the morning of my thirty-second birthday the plate broke in half during heating.
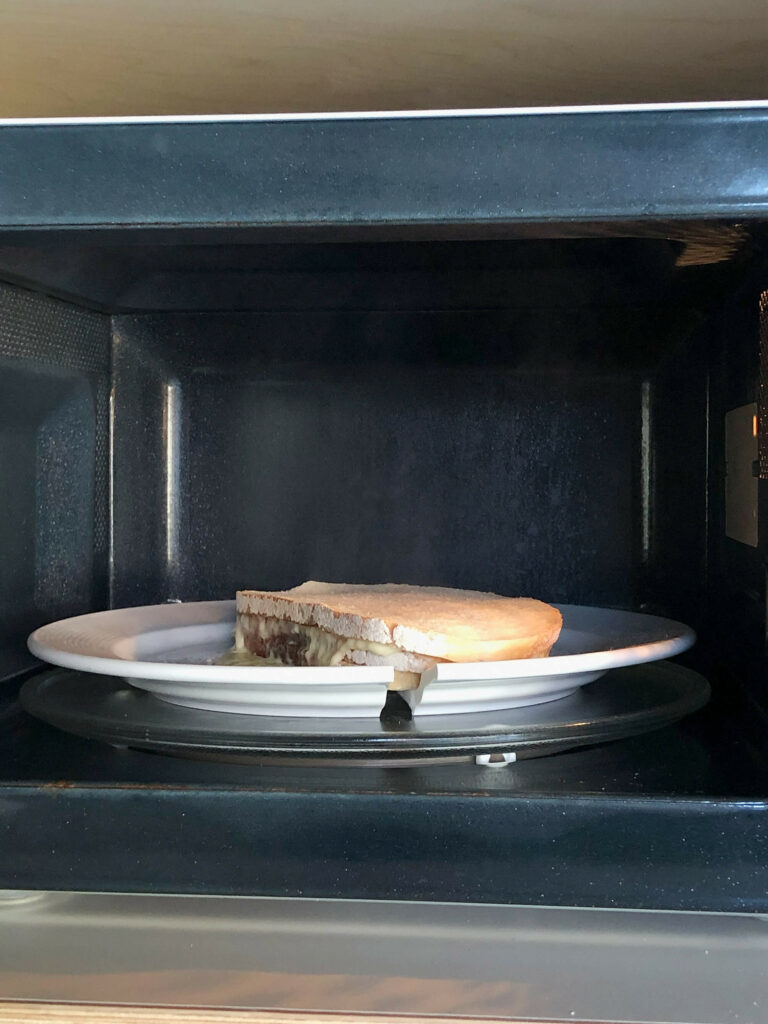

A contraction of smelten (Dutch for melting) and boterham (Dutch for a slice of bread).

Today I brought an old bedspring, the styrofoam the air-humidifier came in, a few bags of sawdust and some scrap pieces of plywood to the municipal recycling center. As I was waiting to mount the stairs to the scrap metal container, a gray-haired man wearing blue leather shoes, dark jeans and a checkered shirt was tipping – with relative ease – a weight bench over the edge of the container.

Holding two cans of spray paint, a city employee walks through a sweet chestnut grove on the graveyard. He’s looking for potholes.

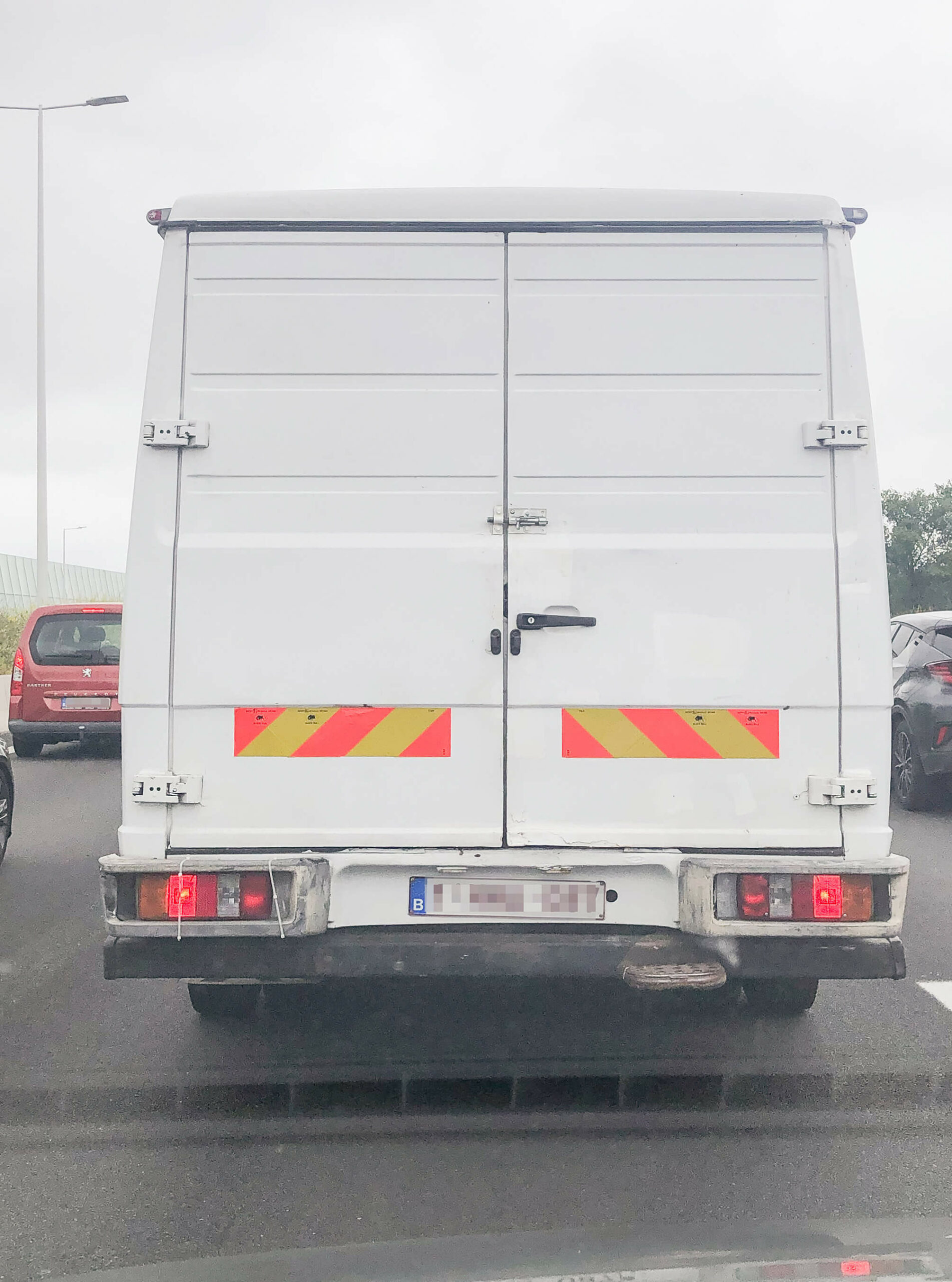
A white Mercedes van inserts in front of me in a traffic jam near Antwerp. The back of the van has been altered in several ways: a latch was added to the door,1 a footstep was bolted to the bumper, a couple of tie-wraps are holding up the lights on the left side.2 Traffic is moving slow. There is no Mercedes logo.3 Some parts have been retouched with white paint that differs slightly from the rest of the bodywork,4 not unlike a tipp-ex’ed document.
Maybe the original locking mechanism no longer functions, or, perhaps, the owner wants to add a padlock to the doors at night.
Maybe a corroded screw caused the lights to come loose, or a slight collision.
Someone might have stolen it. Mercedes stars are often stolen, although mostly from the hood.
Maybe to counter corrosion, to conceal a mark someone made on the van or to cover up a fixed dent.
Legislation concerning the publication of someone else’s licence plate on the internet and the demand to blur it, is somewhat ambiguous.

‘You see?!’
[The man points at the waybill1 on the floor behind the glass door that closes off the abandoned and dismantled hall.]
‘It used to be here, I’m sure.’
[He looks around.]
‘I’m sure.’
[He turns towards me.]
‘Are you also here for the Leen Bakker?2 This used to be a Leen Bakker. I just looked it up on their website. They are open from 9 to 6 today.’
[He points at the waybill again.]
‘It was here. I remember well. It’s been years. But it’s here.’
[He walks away.]
‘I’ll look around.’
The waybill documents the transport of a 30m3 container filled with approximately 5000 kg of waste from this branch of Leen Bakker to a scrap processing company in nearby Ninove. They take care of scrap, both ferrous and non-ferrous metals. They also have a recognized depollution center for end-of-life vehicles.
A chain of furniture and interior stores with branches in the Netherlands, Belgium and the Caribbean part of the Kingdom of the Netherlands.
